[Capas 0, 1, 2 Y 3 De Blockchain: Una Explicación]

Executive Summary

This comprehensive guide delves into the four fundamental layers of blockchain technology: Layer 0, Layer 1, Layer 2, and Layer 3. We’ll unravel the intricacies of each layer, explaining their roles, functionalities, and interdependencies. Understanding these layers is crucial for grasping the potential and limitations of blockchain, and for navigating the increasingly complex landscape of decentralized applications (dApps) and cryptocurrencies. We’ll explore key concepts and provide actionable insights, enabling you to make informed decisions in this rapidly evolving technological field. This article aims to be the definitive resource for anyone seeking a clear and concise understanding of blockchain’s layered architecture.

Introduction
Blockchain technology, while often perceived as a monolithic entity, is actually a multi-layered architecture. Each layer plays a distinct role in facilitating the secure and efficient execution of transactions and the overall functionality of the blockchain network. From the foundational hardware to the application layer, understanding these layers is paramount to appreciating the true potential and complexity of this transformative technology. This article will break down each layer, providing a clear and accessible explanation for both beginners and experienced blockchain enthusiasts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is Layer 0 in blockchain? A: Layer 0 refers to the foundational infrastructure upon which the entire blockchain ecosystem is built. It encompasses the underlying hardware and network protocols that ensure the security and stability of the network.
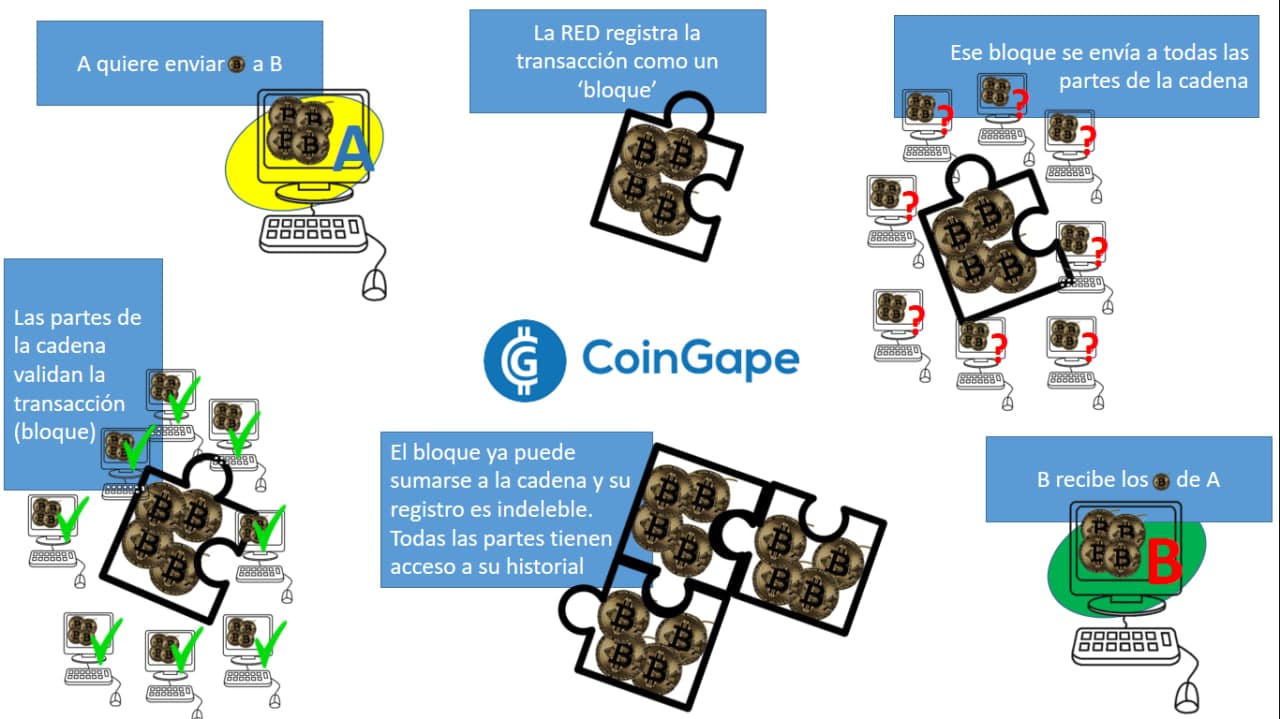
Q: What’s the difference between Layer 1 and Layer 2 blockchains? A: Layer 1 blockchains are the base protocols like Bitcoin and Ethereum, handling the core transaction processing. Layer 2 solutions are built on top of Layer 1 to enhance scalability and reduce transaction costs.
Q: What are some examples of Layer 3 applications? A: Layer 3 encompasses applications built using the functionalities provided by the underlying layers. Examples include decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, non-fungible token (NFT) marketplaces, and supply chain management systems.
Layer 0: The Foundation
Layer 0 represents the physical infrastructure supporting the entire blockchain ecosystem. Think of it as the bedrock upon which everything else is built. This layer ensures the network’s reliability, security, and overall performance.
- Hardware: This includes the servers, data centers, and networking equipment that keep the blockchain running. Powerful hardware is essential for processing transactions and securing the network.
- Network Protocols: This encompasses the communication protocols used by nodes to interact and exchange information, ensuring smooth and efficient data transmission across the network.
- Energy Consumption: The energy required to power and maintain the network is a critical aspect of Layer 0, especially considering environmental concerns surrounding certain blockchains.
- Data Centers and Geographic Distribution: The strategic placement of data centers across different geographical regions enhances network resilience and minimizes latency.
- Security Measures: Robust security protocols are crucial at this layer to protect against various cyber threats and ensure the integrity of the network.
Layer 1: The Core Protocol
Layer 1 is the base layer of the blockchain, where the core protocol resides. It’s responsible for processing transactions, validating data, and maintaining the integrity of the blockchain itself. Think of Layer 1 as the engine driving the entire system.
- Consensus Mechanism: The core protocol dictates how transactions are validated and added to the blockchain. Popular mechanisms include Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS).
- Transaction Processing: This involves verifying transactions, adding them to blocks, and chaining the blocks to form the blockchain.
- Security: Robust cryptographic algorithms and security protocols ensure the integrity and immutability of the blockchain data.
- Scalability: The ability of the Layer 1 protocol to handle increasing numbers of transactions without compromising performance is a crucial factor.
- Decentralization: The degree of decentralization, which impacts security and resistance to censorship, is a defining characteristic of Layer 1 protocols.
Layer 2: Scaling Solutions
Layer 2 solutions are built on top of Layer 1 to address scalability issues. They handle a significant portion of transaction processing off the main blockchain, reducing congestion and improving transaction speeds.
- State Channels: These allow participants to conduct multiple transactions off-chain before settling the final balance on the Layer 1 blockchain.
- Rollups: These bundle multiple transactions together into a single batch and submit them to the Layer 1 blockchain for verification, significantly increasing transaction throughput.
- Sidechains: These are separate blockchains that run parallel to the main Layer 1 blockchain, processing transactions independently before transferring the results back to the main chain.
- Plasma: A framework that allows for the creation of child blockchains that inherit security from the main Layer 1 blockchain.
- Interoperability: The ability for Layer 2 solutions to communicate and interact seamlessly with each other and with the Layer 1 blockchain.
Layer 3: Decentralized Applications (dApps)
Layer 3 is where the real-world applications of blockchain technology are built. These are decentralized applications (dApps) that leverage the functionalities provided by the underlying layers to create innovative solutions across various sectors.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): This encompasses various financial applications built on blockchain, offering decentralized alternatives to traditional financial services.
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): These unique digital assets, often representing ownership of art, collectibles, or other digital items, are created and traded on Layer 3 platforms.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain technology enhances transparency and traceability in supply chains, enabling better tracking of goods and materials.
- Gaming and Metaverse: Blockchain-based games and metaverse platforms offer new possibilities for immersive experiences and player ownership.
- Identity Management: Decentralized identity systems built on blockchain offer greater user control and security over personal data.
Conclusion
Understanding the four layers of blockchain technology is crucial for anyone seeking to navigate this rapidly evolving landscape. From the foundational hardware and network protocols of Layer 0 to the innovative decentralized applications of Layer 3, each layer plays a critical role in shaping the future of this transformative technology. By grasping the interdependencies and unique functionalities of each layer, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions about leveraging blockchain to solve complex problems and drive innovation across various sectors. As the technology continues to mature and evolve, a deep understanding of its layered architecture will be essential for harnessing its full potential. This understanding empowers informed participation, development, and adoption of blockchain-based solutions.
Keywords
Blockchain Layers, Layer 0, Layer 1, Layer 2, Layer 3, Decentralized Applications