Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) are known to be an excellent option to diversify your investment portfolio. They offer a blend of flexibility and broad market exposure, making them appealing to both new and seasoned investors. Here’s a breakdown of why and how ETFs can help diversify your investments:
What Are ETFs?
ETFs are investment funds that pull money from various investors to invest in diversified basket of assets such as stocks, bonds, commodities or other securities. As the name suggests, ETFs are traded on stock exchanges, like individual stocks making them different from Mutual Fund.
Why Diversify with ETFs
- Broad Market Exposure:
ETFs provide instant exposure to multiple securities across various industries or geographies often by tracking indices like the S&P 500, NASDAQ-100, or sector-specific indices. - Cost-Effectiveness:
ETFs generally have lower expense ratios as compared to mutual fund. The passive management style of most ETFs minimizes fees while still delivering solid market performance. - Accessibility:
With ETFs, investors can gain access to hard-to-reach asset classes, such as international equities, real estate, or emerging markets, in a single transaction. - Liquidity:
Since ETFs trade like stocks, they can be bought and sold throughout the trading day, offering greater flexibility than mutual funds, which only settle at the end of the trading day. - Customization:
Whether you’re looking to invest in specific industries, follow ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) principles, or hedge against inflation, there’s likely an ETF tailored to your needs.
Tips for Building a Diversified Portfolio with ETFs
- Choose Different Asset Classes:
Combine equity ETFs, bond ETFs, and commodity ETFs to spread risk across various asset types. - Consider Geographic Diversification:
Include domestic and international ETFs to mitigate risks tied to one country’s economy. - Factor in Sectoral Balance:
Look for sector-specific ETFs to invest in technology, healthcare, energy, or other industries while ensuring no single sector dominates your portfolio. - Mind the Fees and Liquidity:
Opt for ETFs with low expense ratios and sufficient trading volume to avoid excessive costs or difficulty buying/selling shares. - Stay Aligned with Your Goals:
Select ETFs that match your risk tolerance, investment horizon, and financial objectives. For instance, if you’re saving for retirement, long-term growth ETFs might be more suitable.
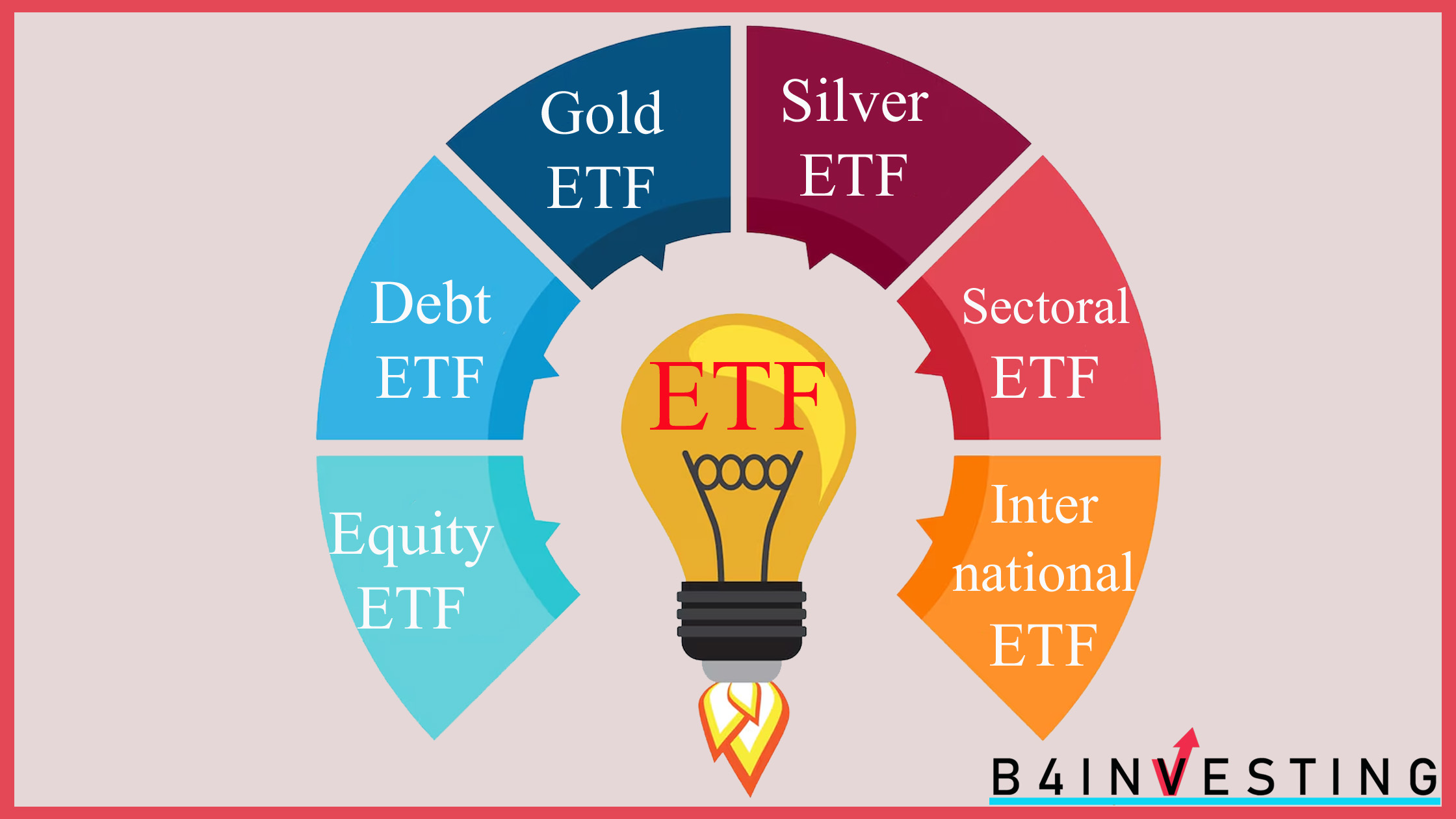
Popular ETF Categories
In India, the ETF market is growing rapidly, offering investors a variety of options. Here’s a breakdown of the primary types of ETFs available:
1. Equity ETFs:
- These are the most common type, tracking various stock market indices. Examples include:
- ETFs tracking broad market indices like the Nifty 50 and Sensex.
- Sectoral ETFs focusing on specific industries such as banking (Nifty Bank ETF), IT, or pharmaceuticals.
- Market capitalization-based ETFs (large-cap, mid-cap, small-cap).
- Smart Beta ETFs: These use factor based investing, like momentum, value, or low volatility.
- ESG ETFs: that focus on Environmental, social, and governance factors.
2. Debt ETFs:
- These ETFs invest in fixed-income securities, such as government bonds and corporate bonds.
- They provide exposure to the debt market and can offer stability to a portfolio.
- Target maturity debt etfs, have become very popular.
3. Commodity ETFs:
- These ETFs track the prices of commodities, primarily:
- Gold ETFs: These are very popular in India, offering a way to invest in gold without physically holding it.
- Silver ETFs: are also available.
4. International ETFs:
- These ETFs provide exposure to international markets, allowing Indian investors to diversify their portfolios globally.
Read also: Large Cap vs Small Cap vs Mid Cap Funds
ETF vs. Mutual Fund vs. Stocks
| Feature | ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds) | Mutual Funds | Stocks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trading | Traded on exchanges (NSE, BSE) throughout the day. | Traded once daily, based on NAV. | Traded on exchanges (NSE, BSE) throughout the day. |
| Pricing | Prices fluctuate throughout the day. | Priced at the end of the day (NAV). | Prices fluctuate throughout the day. |
| Diversification | Diversified (tracks indices, sectors). | Diversified (managed portfolio). | Concentrated (single company). |
| Management | Primarily passive (index tracking). | Active or passive. | Self-managed. |
| Expense Ratios | Generally lower. | Varies, often higher. | No expense ratios (brokerage fees apply). |
| Liquidity | High liquidity. | Liquid, but end-of-day transactions. | High liquidity, but varies. |
| Costs | Brokerage fees, low expense ratio. | Expense ratios, potential loads. | Brokerage fees, STT. |
| Taxation | Taxed as equity or debt depending on underlying assets. | Taxed as equity or debt depending on underlying assets. | Capital gains tax, dividend tax. |
| Popularity in India | Growing popularity, especially index and gold ETFs. | Very popular, SIP investments are common. | Growing retail participation. |
| Regulatory Body | SEBI | SEBI | SEBI |
Conclusion
ETFs are a versatile and powerful investment tool that can help you achieve a diversified portfolio with ease. By strategically selecting ETFs that align with your financial goals, you can minimize risk, enhance returns, and enjoy the flexibility that comes with this modern investment vehicle. Always research thoroughly or consult a financial advisor to ensure your choices fit your specific investment strategy.